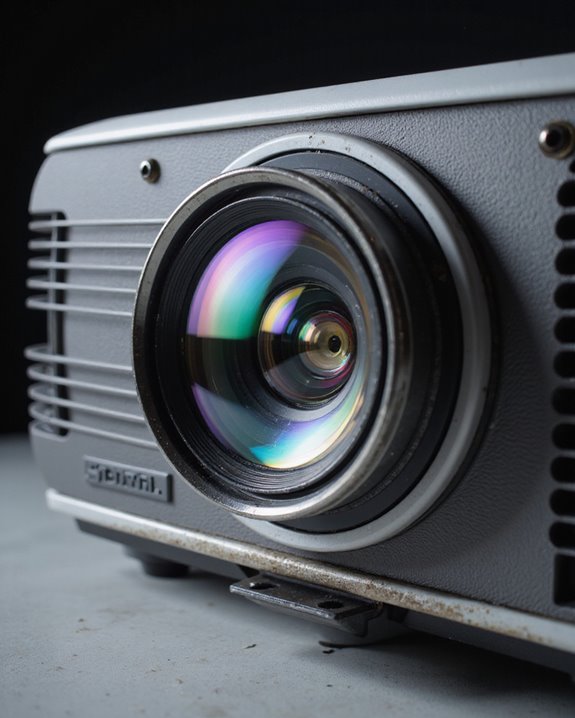
A projector lens uses precisely arranged glass or plastic elements to bend and focus light from the projector’s source, projecting a sharp image onto a screen. Key features include: focus and zoom rings for image clarity and size adjustment; throw ratio, which compares screen width to projector distance; and anti-reflective coatings to boost brightness. Uniform sharpness and minimized color distortion are achieved through advanced lens geometry. Exploring further reveals how these features maintain high image quality in various viewing conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Projector lenses use precisely arranged optical elements to bend and focus light, creating clear and sharp images on a screen.
- Adjustable features like focus, zoom, and lens shift allow users to fine-tune image size, clarity, and position without moving the projector.
- Optical coatings and high-quality glass reduce glare, reflections, and color distortions for superior brightness and image fidelity.
- The throw ratio and focal length determine how large an image appears at different distances from the screen.
- Mechanical and optical design minimize distortions, ensuring uniform sharpness and consistent image quality across the entire projection area.
Anatomy and Components of a Projector Lens
A projector lens is a carefully engineered assembly designed to focus and project light onto a screen, using multiple specialized components. Its main structure, called the lens barrel, houses and protects delicate optical elements. Lens materials are critical—high-quality optical glass or durable plastics are used, shaped and polished through advanced manufacturing processes for maximum clarity. Key components include:
- Multiple lens elements, often grouped for focus or zoom adjustments.
- Aperture and iris mechanisms, which control light flow and image brightness.
- Focus and zoom rings, offering precise manual or motorized adjustments.
- Locking latches and shift mechanisms for secure positioning and alignment.
- Additionally, the dust-proof design of the lens assembly helps maintain optimal performance over time by preventing debris accumulation. Optical coatings are applied to lens surfaces, reducing glare and protecting against dust or scratches. Each part ensures reliable, high-quality image projection.
The Role of Lens Elements in Image Formation
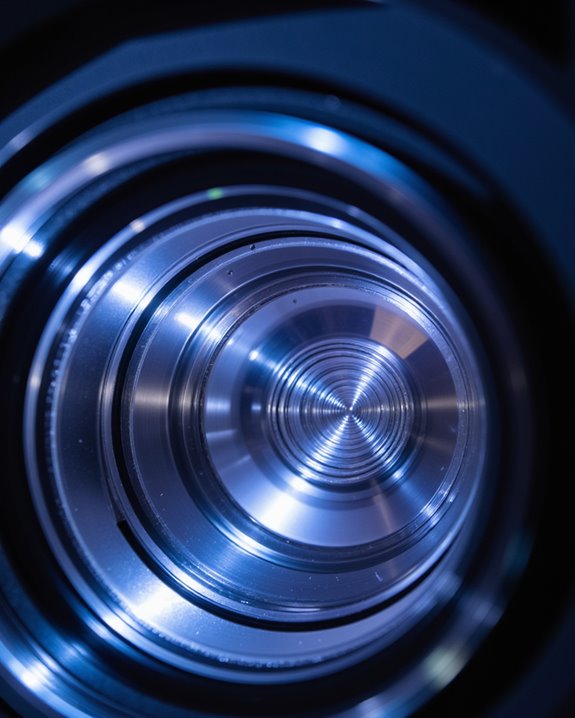

Projector lens elements determine how light is shaped into a clear, sharp image on the screen. Each element, precisely arranged, bends (refracts) light from the projector’s source. This process uses laws of refraction to focus and magnify the image from a slide or digital modulator onto the image plane. Lens coating—thin optical layers applied to lens surfaces—reduces reflections and light loss, improving brightness and clarity. It also helps minimize chromatic aberration, a color distortion caused when light wavelengths focus at different points. Key roles of lens elements include:
- Magnifying and properly orienting the image
- Ensuring efficient light transmission
- Maintaining sharpness and high resolution
Condenser lenses provide even illumination, while projection lenses collect and project the final image. High-quality lens elements are essential for accurate image formation.
Focusing, Alignment, and Adjustability

While image clarity remains the top priority in projection systems, focusing, alignment, and adjustability features within projector lenses make this possible across a wide range of environments. Focus calibration is achieved through manual or automatic adjustments. Automatic systems use sensors and microprocessors to analyze image sharpness, adjusting lens position as needed. Manual focus relies on physically moving lens parts. Lens shift technology enables vertical or horizontal repositioning of the image without moving the projector, providing flexibility in placement. Zoom lenses adjust image size and placement, whereas fixed lenses cannot. Peripheral focus adjustment guarantees edge-to-edge sharpness. Regular lens cleaning is vital, as dust and debris can affect focus and alignment. Durable, heat-resistant materials and strong mounts reduce focus drift, maintaining consistent performance over time. Incorporating high-quality optics and advanced lens technology further enhances image sharpness and clarity.
Interpreting Key Projector Lens Specifications
How can one make sense of the different numbers and features listed in projector lens specifications? The most important is the throw ratio, which is the ratio of the distance from projector to screen (throw distance) divided by the screen’s width. A zoom ratio shows how much the lens can change image size without moving the projector. Lens shift allows for moving the image up, down, or sideways, while keeping the projector still. The aperture, marked as f-number, tells how much light passes through—the lower the number, the brighter the image. Focal length affects how wide an image appears at a given distance. Lens material quality and regular lens cleaning both play a role in delivering a sharp, clear image, especially as lens options vary by projector type.
Managing Optical Challenges for Superior Image Quality

Achieving a sharp and accurate projected image depends on how well the lens manages common optical challenges. Optical distortions, such as spherical distortion and chromatic aberrations—where different colors focus at slightly different points, causing color fringing—are minimized using aspheric lens elements and carefully selected materials. Mechanical stability, meaning the lens holds its shape and alignment during use, is essential to maintain consistent performance. To further combat image blur and uneven focus, flat-field lens designs provide uniform sharpness across the entire projection.
Key methods for superior image quality include:
- Anti-reflective coatings to reduce light scatter and improve contrast.
- Maintaining consistent brightness by managing zoom lens throw ratios.
- Optimizing lens geometry to minimize pincushion distortion.
Engineers continually refine these elements to balance sharpness, brightness, and color fidelity.
Practical Tips for Selecting and Maintaining Projector Lenses

Selecting and maintaining the right projector lens is essential for producing clear, sharp images in any projection environment. Lens selection should be based on projection distance, image size needs, and environmental factors. Long distance projections require lenses with narrow beam angles (5°–15°), while short distance applications use wider angles (20°+). Standard lenses offer minimal distortion, whereas telephoto lenses reduce noise and environmental interference. Key specifications—such as focal length, working distance, and field of view—must be matched to projector and screen size. Lens coating, a thin protective layer, reduces glare and prevents scratches. Aperture control, the ability to adjust lens opening, manages image brightness and clarity. Maintenance includes regular cleaning, using lens caps, and checking alignment to ensure lasting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Projector Lenses Be Upgraded or Replaced With Third-Party Options?
Projector lenses can be upgraded or replaced with third-party options, but compatibility challenges exist due to differences in lens material and focal length adjustment. Thorough compatibility checks and professional installation are often recommended to guarantee ideal performance and image quality.
How Do Projector Lenses Compare to Camera Lenses in Design?
While camera lenses chase the elusive muse of depth of field and artistic blur, projector lenses scoff, favoring lens focality and optical clarity for sheer brightness. Their utilitarian design prioritizes even projection over nuanced photographic finesse.
Are Projector Lenses Compatible Across Different Projector Brands?
Brand compatibility and lens interchangeability are extremely limited among projector manufacturers. Proprietary mounts, specialized optics, and electronic controls generally prevent projector lenses from being swapped across brands without adapters, modifications, or risking compromised image quality and invalidated warranties.
What Environmental Factors Can Affect Projector Lens Performance?
Projector lens performance is influenced by environmental factors such as ambient light, which affects image visibility, and dust accumulation, which degrades brightness and color accuracy. Temperature, moisture exposure, and particulate matter also impact lens function and longevity.
Do Projector Lenses Require Calibration After Transportation or Relocation?
Projector lenses often require calibration after transportation or relocation to maintain image quality. Calibration involves alignment adjustment and may include lens cleaning, ensuring proper focus, zoom, and image alignment, while preventing misalignment issues caused by movement or handling.